Key Takeaways
- Geothermal heating systems utilize the Earth’s stable underground temperatures for highly efficient home heating.
- Compared to conventional options, these systems can reduce electricity consumption by up to 15% and lower CO₂ emissions by 50%–70%.
- Technological advancements like AI and Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) are driving efficiency and expanding adoption.
- Government policies and incentives are accelerating geothermal system deployment worldwide.
Introduction
Geothermal heating systems are rapidly changing the landscape of home energy, setting new standards in sustainability and cost-effectiveness. Utilizing the Earth’s relatively constant underground temperature, a geothermal home system provides consistent heating while reducing energy bills and slashing greenhouse gas emissions. These systems operate quietly below the ground, making them nearly invisible while offering tangible benefits to homeowners and the environment.
The appeal of geothermal heating isn’t just its environmental friendliness—it’s also about long-term savings, robust system life, and the ability to integrate with evolving technology. As more homeowners and policymakers seek alternatives to fossil fuel-based heating, geothermal systems stand out as reliable, future-proof solutions that contribute to a cleaner planet and increased home comfort.
Understanding Geothermal Heating Systems
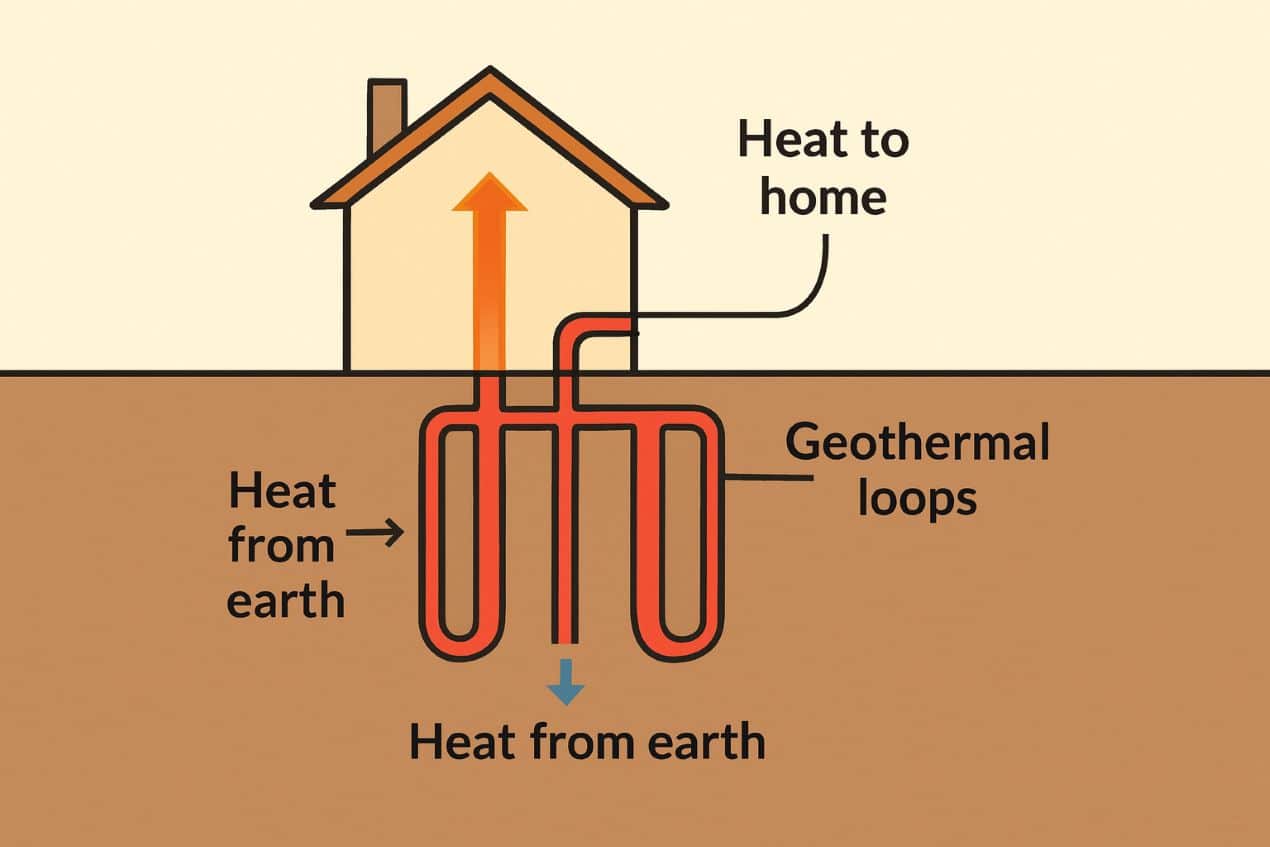
Geothermal heating systems, known as ground-source heat pumps, leverage the Earth’s stable core temperature. A series of underground pipes loops through your property, drawing warmth from the earth during colder months and dispersing heat into the ground during warmer months. This process happens well below the frost line, ensuring reliable performance in nearly any climate. Unlike air-source heat pumps impacted by outside temperature swings, geothermal setups maintain high efficiency year-round.
These systems offer heating and cooling capabilities, providing an integrated solution for total home comfort. The simplicity of the system’s design—primarily involving just one moving part, the ground loop—means lower maintenance and much less wear and tear, which translates to reduced lifetime costs for homeowners.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
One of the most compelling cases for geothermal heating systems is their remarkable energy efficiency. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, geothermal heat pumps can reduce energy usage by as much as 15% compared to standard heating methods, delivering notable cost savings on monthly energy bills. Beyond cost, these systems dramatically curb greenhouse gas emissions—providing a reduction of 50–70% in CO₂ output compared to fossil fuel-based options. As such, geothermal is a crucial technology in pursuing carbon-neutral homes.
Technological Advancements Enhancing Geothermal Systems
In recent years, we have seen exciting innovations in geothermal energy. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is now being integrated to provide real-time system diagnostics, automated optimization, and preventative maintenance alerts—making these systems even more efficient and user-friendly. Meanwhile, Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) technology is opening doors in areas previously unsuitable for geothermal by allowing engineers to access heat from complex rock layers deep underground. This evolution is widening the reach and practicality of geothermal heating, making it a realistic choice for a broader range of climates and home types.
Government Initiatives and Policies
As the global focus intensifies on reducing fossil fuel dependence, governments worldwide are taking action to accelerate geothermal adoption. Germany’s move to streamline geothermal project approvals and aim for a fossil fuel-free heating sector by 2045 is a significant milestone. The European Union is encouraging member nations to leverage geothermal for energy security and emissions reduction. Incentives, rebates, and favorable policies are making these systems more accessible to homeowners, often tipping the scales on initial investment decisions.
Economic Considerations and Return on Investment
While the upfront installation cost for geothermal heating systems can be higher than for traditional systems, homeowners regularly recoup that investment within 5–15 years. This payback comes from reduced utility bills, minimal maintenance, and a long system lifespan (typically 30–50 years). Additionally, government tax credits, local rebates, and various financing options can dramatically offset initial expenses, making geothermal an increasingly attractive financial choice.
Real-Life Applications and Success Stories
Communities and neighborhoods are already demonstrating the transformative power of geothermal systems. In Framingham, Massachusetts, for example, a networked geothermal pilot project is setting up centralized geothermal service for nearly 40 buildings, including affordable housing and local businesses. The goals are decarbonization, cost savings, and proving scalability for neighborhood-wide, sustainable heating systems. Such successful pilots are paving the way for mass adoption and greater climate resilience in cities and towns across the globe.
Future Outlook and Potential
The outlook for geothermal heating is stronger than ever. Continued advancements in drilling technology, smart controls, and energy storage are making these systems increasingly adaptable and efficient. Government mandates for clean energy and consumer demand for sustainable alternatives fuel market growth. As more property owners value long-term efficiency, resilience, and environmental stewardship, geothermal is poised to play a foundational role in the global shift toward sustainable living.
In summary, geothermal heating systems represent a powerful combination of environmental benefit, economic value, and technological promise. By harnessing the Earth’s steady temperature, these systems are leading the transition to a cleaner, more efficient future, one home at a time.